
Hard disk health test manual#
Windows 10 is set to run chkdsk automatically, so you may be alerted to issues before you do a manual run of this utility. In this scenario the C: drive is an NvME SSD and D: is the higher-capacity hard drive that requires servicing. That command tells the utility to check only your D drive. The /F option also needs a reboot to run but requires less time.Īn example command might be chkdsk d: /r. The /R option can take a very long time to complete, and needs to work on a reboot so only run that when you have the time. The /F option focuses on fixing filesystem errors, while the /R option also checks for bad physical sectors on the drive-don’t use the /R option on an SSD as this option is not built for solid state drives. If you want it to fix problems you need to run the check disk program with the /F or /R options. To just check the status of all your drives type chkdsk for a read-only status of your drives. Either its end is near, or it’s going to start malfunctioning soon. If you start to hear a grinding noise emanating from your PC, for example, that is mostly likely the hard drive.

While SMART is a useful tool for monitoring your drive’s health, you should also keep an eye on how your drive behaves and sounds. HDD interiors almost resemble a high-tech record player.
Hard disk health test software#
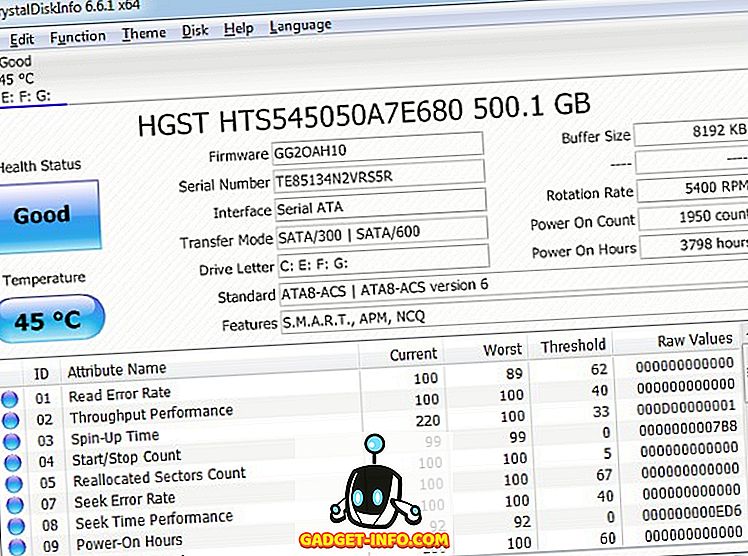
The best solution right now for SSDs is to use monitoring tools provided by the drive maker such as Crucial’s Storage Executive, WD’s SSD Dashboard, or Samsung’s Magician Software (for EVO 860 and up). SMART is also a part of SSDs, but it has the same drawbacks and limitations as hard drives. In other words, your particular drive might report issues before failing, or it might not. Statistically speaking the majority of discs do report SMART issues before failing however, statistics become less reliable when trying to predict the fate of a single drive. In 2016, Backblaze reported that it was seeing 23.3 percent of its data center drives failing without reporting issues from the five SMART attributes it tracks. Open a Windows command prompt and enter the following: wmic diskdrive get model,status. This basic tool is a simple yay/nay health result based on the SMART statistics. The simplest way is to use the Windows command line utility WMIC, which stands for Windows Management Instrumentation Command-line (utility). Most of the time the SMART system works in the background, but you can bring it to the fore in a number of ways. Drive manufacturers can take their own approaches to SMART, but they generally measure similar performance points such as read error rates, mechanical shock, hard disk temperature, seek time performance, and so on. This system is built into most modern hard drives and SSDs, and it’s designed to report when your drive is failing or encountering issues. The first tool for keeping tabs on a hard drive is its Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology, or SMART, feature. While you can’t always predict when or how your hard drive will bite the dust, you can take a few steps to see it coming.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
